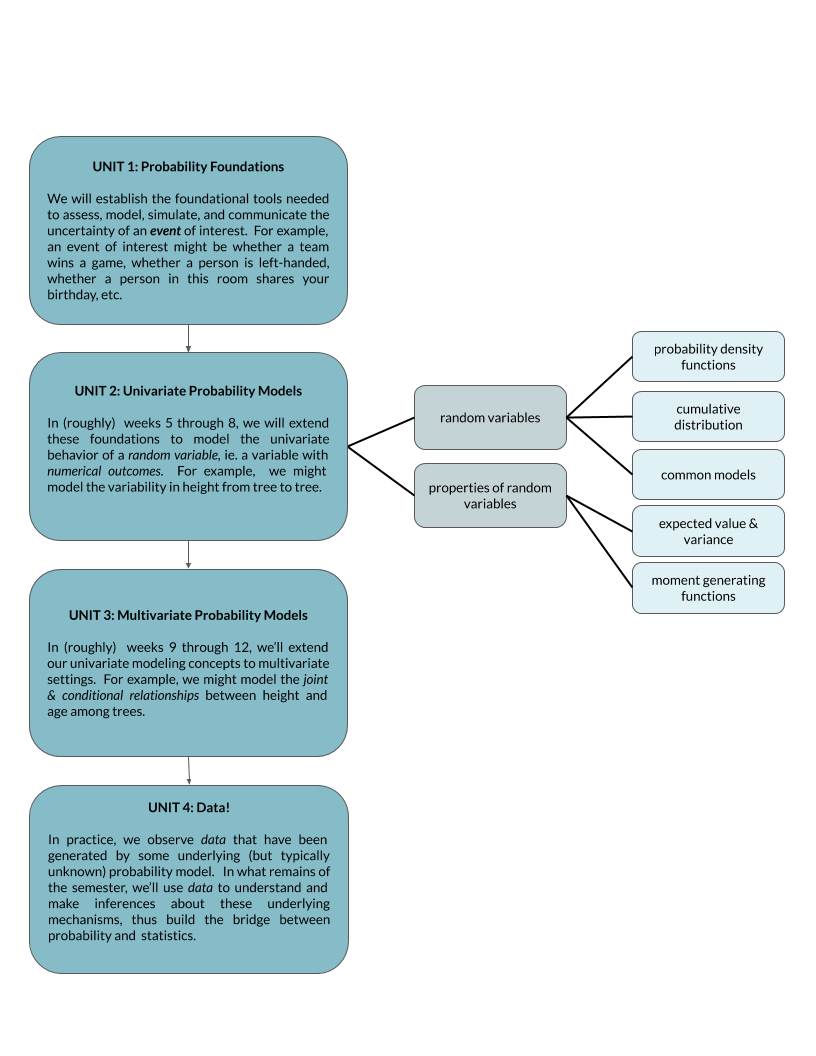
Unit 2 overview
Random Variables
A random variable \(X\) is a function from the sample space \(S\) to the real line \(\mathbb{R}\). That is, \(X\) is a numerical outcome of an experiment. There are two types of RVs:
- \(X\) is discrete if the list of possible outcomes of \(X\) is finite or countably infinite.
- \(X\) is continuous if the list of possible outcomes of \(X\) is uncountably infinite (eg: an interval).
RANDOM VARIABLES IN CONTEXT
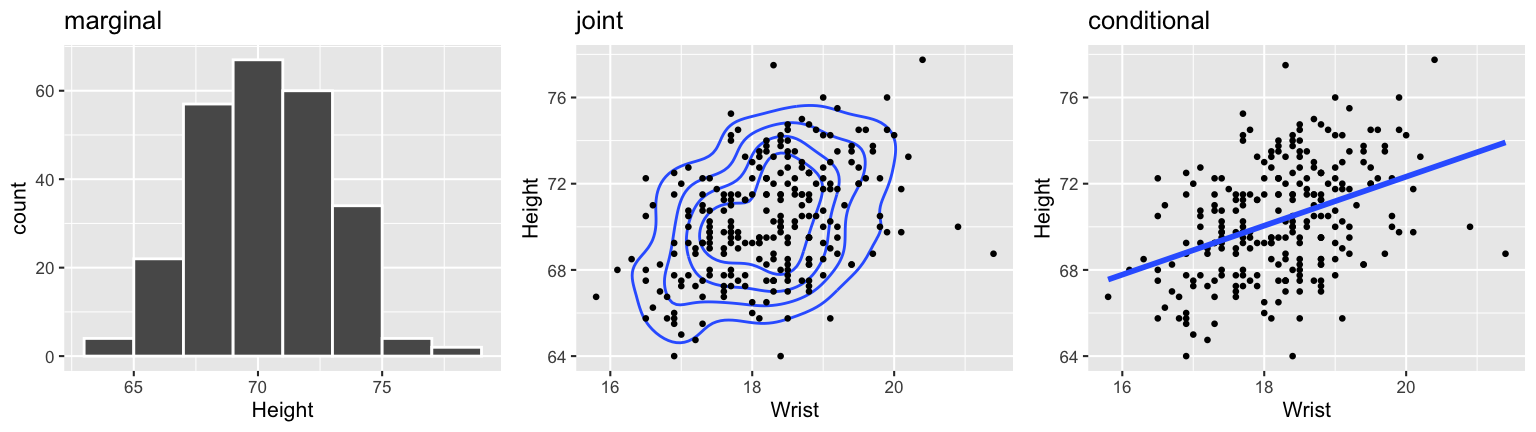
Throughout Units 2 and 3, we’ll consider three types of random variable models that can be used to answer three types of questions. First, let \(X\) be the wrist circumference and \(Y\) be the height of an adult.
Univariate models: \(Y\)
How does height vary among adults?Joint models: \(Y\) and \(X\)
What’s the joint behavior, or typical combination, of wrist and height among adults?Conditional models: \(Y\) vs \(X\)
How does height depend upon wrist?